Distribute Hosted Cluster workloads
Topology
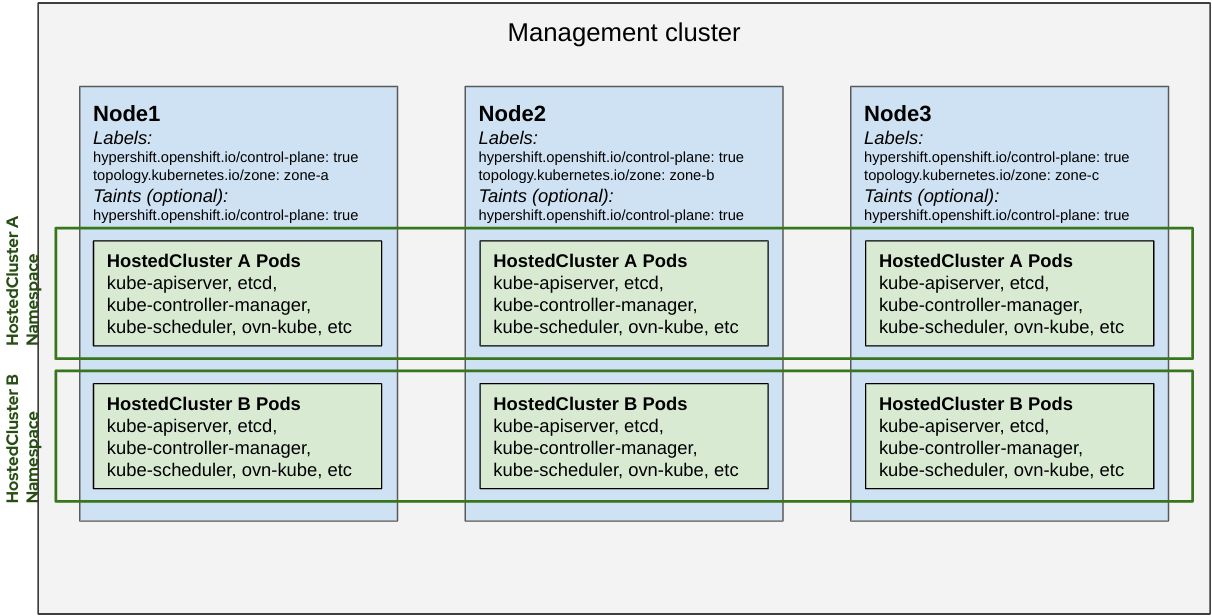
HyperShift enables implementing the strategy to colocate and isolate pods for Hosted Clusters. As a management cluster operator you can leverage the following Node labels and taints:
hypershift.openshift.io/control-plane: true
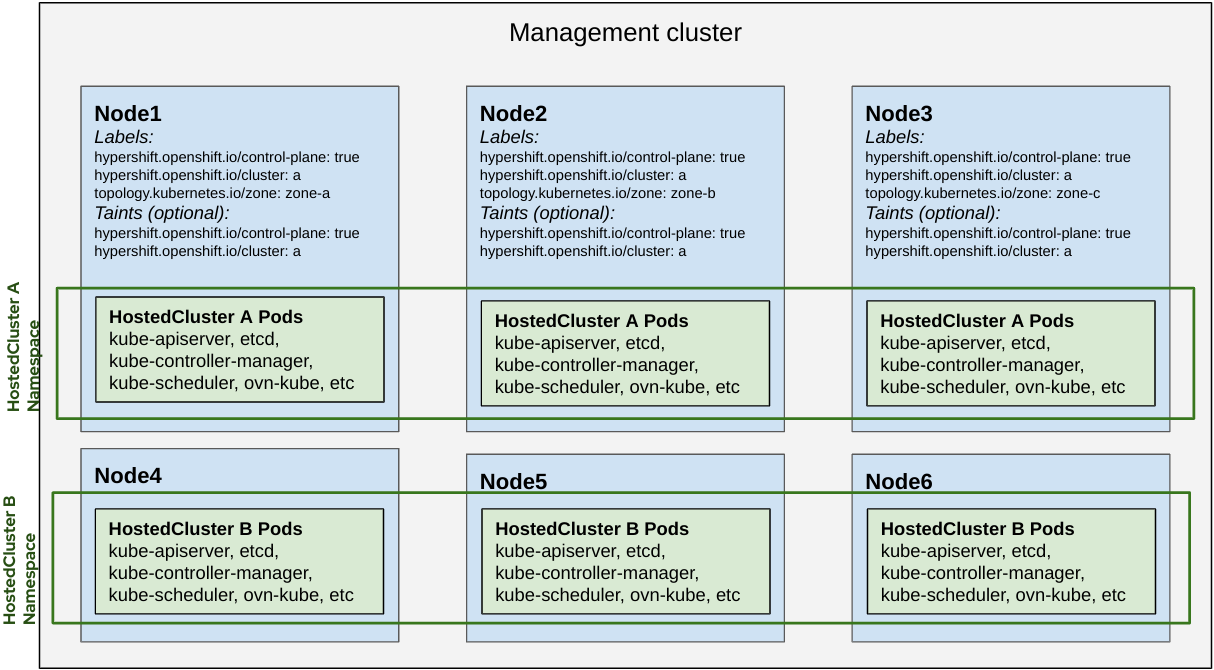
hypershift.openshift.io/cluster: ${HostedControlPlane Namespace}
- Pods for a Hosted Cluster tolerate taints for "control-plane" and "cluster".
- Pods for a Hosted Cluster prefer to be scheduled into "control-plane" Nodes.
- Pods for a Hosted Cluster prefer to be scheduled into their own "cluster" Nodes.
In addition:
- Pods for a Hosted Cluster prefer to be scheduled into the same Node.
- If the
ControllerAvailabilityPolicyisHighlyAvailablePods for each Deployment within a Hosted Cluster will require to be scheduled across different failure domains by settingtopology.kubernetes.io/zoneas the topology key. - A HostedCluster can require their Pods to be scheduled into particular Nodes by setting
HostedCluster.spec.nodeSelector. E.gspec: nodeSelector: role.kubernetes.io/infra: ""
Custom Taints and Tolerations
By default, pods for a Hosted Cluster tolerate the "control-plane" and
"cluster" taints, however it is also possible to use custom taints on
nodes and allow Hosted Clusters to tolerate those taints on a per
Hosted Cluster basis by setting HostedCluster.spec.tolerations. E.g
spec:
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: kubernetes.io/custom
operator: Exists
Tolerations can also be set on the Hosted Cluster while creating a cluster
using the --tolerations hcp cli argument. E.g
--toleration="key=kubernetes.io/custom,operator=Exists,effect=NoSchedule"
Usage of custom tolerations in concert with nodeSelectors allows for fine granular control of Hosted Cluster pod placement on a per Hosted Cluster basis. This control allows for groups of Hosted Clusters to be colocated and isolated from other Hosted Clusters. It also allows for custom placement of Hosted Clusters within infra and master nodes.
Scheduling Topology Options
Cluster Service Providers may choose how hosted control planes are isolated or co-located. The three different options are:
- Shared Everything
- Shared Nothing
- Dedicated Request Serving
These options can be seen as a spectrum of isolation. Shared Everything is the least isolated, Dedicated Request Serving (Shared Some) and then Shared Nothing being the most isolated option.
NOTE: Each hosted control plane can run Single Replica or Highly Available. If Highly Available, the control plane will be spread across failure domains via topology.kubernetes.io/zone as the topology key.
Shared Everything
- All hosted control plane pods are scheduled to any node that can run hosted control plane workloads.
- Nodes can be allocated specifically for control plane workloads by tainting and labeling them with
hypershift.openshift.io/control-plane: true.
Shared Nothing
- To confine nodes to a specific hosted cluster taint and label them with
hypershift.openshift.io/clustervalue. - No other control plane pods will land on those nodes.
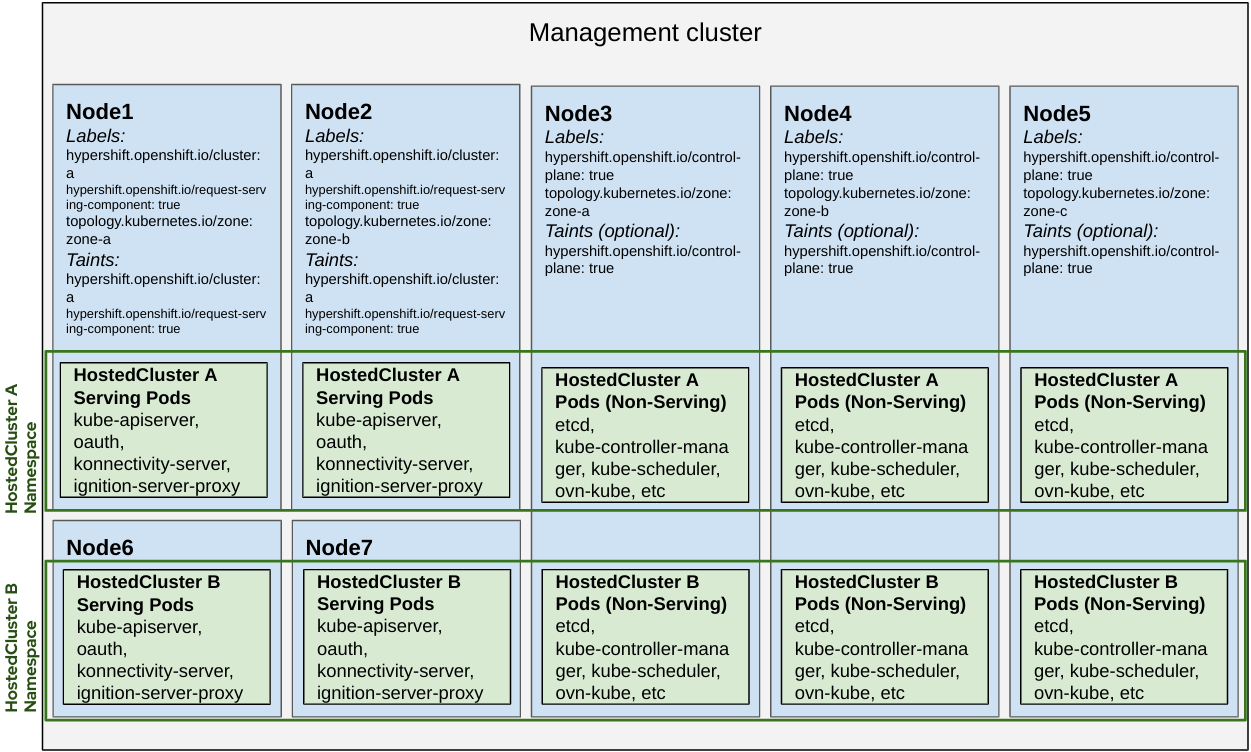
Dedicated Request Serving
- Two nodes in different zones are dedicated to a specific hosted cluster’s front end serving components.
- The rest of the hosted cluster’s control plane pods can co-exist with other clusters’ control plane pods running on shared nodes.
- When running a Highly Available control plane, there will only be 2 replicas of request serving workloads instead of 3.
NOTE: A HostedCluster must have:
hypershift.openshift.io/topology: dedicated-request-serving-componentsannotation to honor dedicated serving content workloads affinity opinions.- nodeSelector set as
hypershift.openshift.io/control-plane: truefor it to be a hard requirement for workloads to be scheduled. Without it that label is a soft requirement meaning workloads will try to find any suitable node if there’s none with this label.
Priority
HyperShift leverages PriorityClasses for driving Priority and Preemption of their managed Pods. It will install four priority classes in a management cluster with the following order of priority from highest to lowest:
hypershift-operator: Hypershift operator podshypershift-etcd: Pods for etcd.hypershift-api-critical: Pods that are required for API calls and resource admission to succeed. This includes pods like kube-apiserver, aggregated API servers, and webhooks.hypershift-control-plane: pods in the HyperShift Control Plane that are not API critical but still need elevated priority. E.g Cluster Version Operator.